Phishing attacks have shifted; it’s no longer about volume, it’s about precision. These sites may look harmless, but the emails delivering them still rely on a familiar formula. Urgent language. Faked sender details. Links like these are designed to pass through security filters, and many do.
That’s why protection against phishing attacks in 2025 takes more than awareness training. Spotting red flags helps, but it’s not enough. You need to understand how phishing works now, how the tactics have changed, and why traditional defenses often miss them.
Email is still the most straightforward way in. These attacks can lead to wire fraud, credential theft, malware infections, or full-scale business email compromise.
In this guide, we’ll break down how phishing attacks in emails work, the most common types targeting businesses, and the steps you can take to protect your users and your data.
Subscribe to our Behind the Shield Newsletter.
What Is Email Phishing & How Does This Scam Work?


Phishing attacks now account for over 22% of all cybercrime. In 2025, they're not just common, they're constant. The FBI received 193,407 phishing-related complaints last year alone.
It’s important to demystify phishing attacks to better understand how they work. Phishing emails impersonate people you trust — vendors, coworkers, even your own boss — to get you to act before thinking. Maybe hand over a password, open a file you weren’t expecting, or send money to the wrong place.
Most phishing campaigns are after sensitive information: financial details, login credentials, and company data. Some attackers still send generic spam to thousands of people, but more are shifting to targeted emails that feel personal and credible.
Today’s phishing attacks often use social engineering, and in many cases, AI. Messages are timed well, written clearly, and crafted to sound familiar. They don’t feel like scams. They feel like routine communication. That’s the trap.
It works because it’s cheap, fast, and hard to trace for attackers; launching a campaign costs next to nothing. For the targets, the damage can be lasting, including stolen data, compromised systems, weeks of downtime, and real reputational harm.
Common Phishing Attack Types in 2025 (With Real Examples)


Since 1987, phishing attacks have evolved into a set of highly targeted, professional-grade scams built to steal valuable data. Some of the most pervasive modern types of phishing attacks include:
- Standard Email Phishing: Arguably the most notorious form of phishing, this attack is an attempt to steal sensitive information via an email that appears to be from a legitimate, trusted source. Standard email phishing is not a targeted attack and is often conducted en masse.
- Spear Phishing: The truth is that the anatomy of a spear phishing attack is that they’re engineered. Attackers might pose as a trusted vendor, manager, or colleague and reference a recent project or request urgent action — “Can you review this invoice?” or “I need those login credentials now.” Even the tone and timing can feel eerily real. It’s not just a scam. It’s a simulation of trust.
- Malware Phishing: This attack utilizes the same techniques as typical email phishing; however, malware phishing attacks aim to trick targets into clicking a link or downloading an attachment so malware can be installed on their devices. With criminals leveraging AI-powered email generation and publicly available personal data, malware phishing is currently one of the most pervasive types of phishing attacks.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC): Attackers gain access to a company email account, often an executive’s, and use it to impersonate them. The goal? Trick employees, partners, or customers into wiring money or handing over sensitive info.
- Clone Phishing: An attacker takes a real email you’ve already received and swaps the legit attachment or link with a malicious one. Then they send it to your contacts, posing as you. It looks familiar. That’s the trap.
- Man-In-The-Middle (MITM): An attacker gets in the way of traffic between you and a website and reads or adds data without you knowing. It doesn't need a false network; all it needs is public Wi-Fi that everyone can use. They are on the same connection as you and can watch what you do, steal your login information, or send you to a bogus site. Everything seems fine. That's the risk.
How to Stop Phishing Emails in 2025: Tips & Best Practices
Want to know how to stop phishing attacks in emails before they reach your users? It starts with sharpening awareness and reinforcing habits that recognize the signs before they’re too late.
Visual Red Flags: What to Look For on the Surface
- Typos and strange grammar are still worth watching for. While many phishing emails look polished today, poorly written ones still make it through. If the language feels sloppy, slow down.
- Compare the subject to the message itself. If one sounds urgent and the other feels oddly vague or out of character, that mismatch could mean something’s off.
- Take a close look at the sender. Not the display name — the actual email address. A misspelled domain or extra character is a common trick. It’s easy to overlook in a rush.
Behavioral Clues: Trust Your Instincts
- If something about the message feels wrong, don’t reply. Use a trusted contact method instead. Start a fresh thread or call them directly. That quick pause can stop an attack.
- Never open a file or click a link you weren’t expecting. It’s fine to double-check with the sender. If they’re legitimate, they won’t mind waiting.
- Context matters. Ask yourself: Was this message expected? Does it make sense right now?
When in Doubt: Pause and Verify
- AI-written emails are getting harder to detect. If the tone feels a little too polished or just not quite like the sender, that discomfort is worth listening to.
- Watch for small inconsistencies. A subject about shipping, but the body talks about password resets? That’s a red flag. Don’t dismiss it.
Behavioral Clues: Trust Your Instincts
- If something about the message feels wrong, don’t reply. Use a trusted contact method instead. Start a fresh thread or call them directly. That quick pause can stop an attack.
- Never open a file or click a link you weren’t expecting. It’s fine to double-check with the sender. If they’re legitimate, they won’t mind waiting.
- Context matters. Ask yourself: Was this message expected? Does it make sense right now?
When in Doubt: Pause and Verify
- AI-written emails are getting harder to detect. If the tone feels a little too polished or just not quite like the sender, that discomfort is worth listening to.
- Watch for small inconsistencies. A subject about shipping, but the body talks about password resets? That’s a red flag. Don’t dismiss it.
Spotting phishing is less about following a checklist and more about noticing when something doesn’t sit right. Familiar habits, slowing down, reading carefully, and checking sources, are your first line of defense.
Practical Exercise
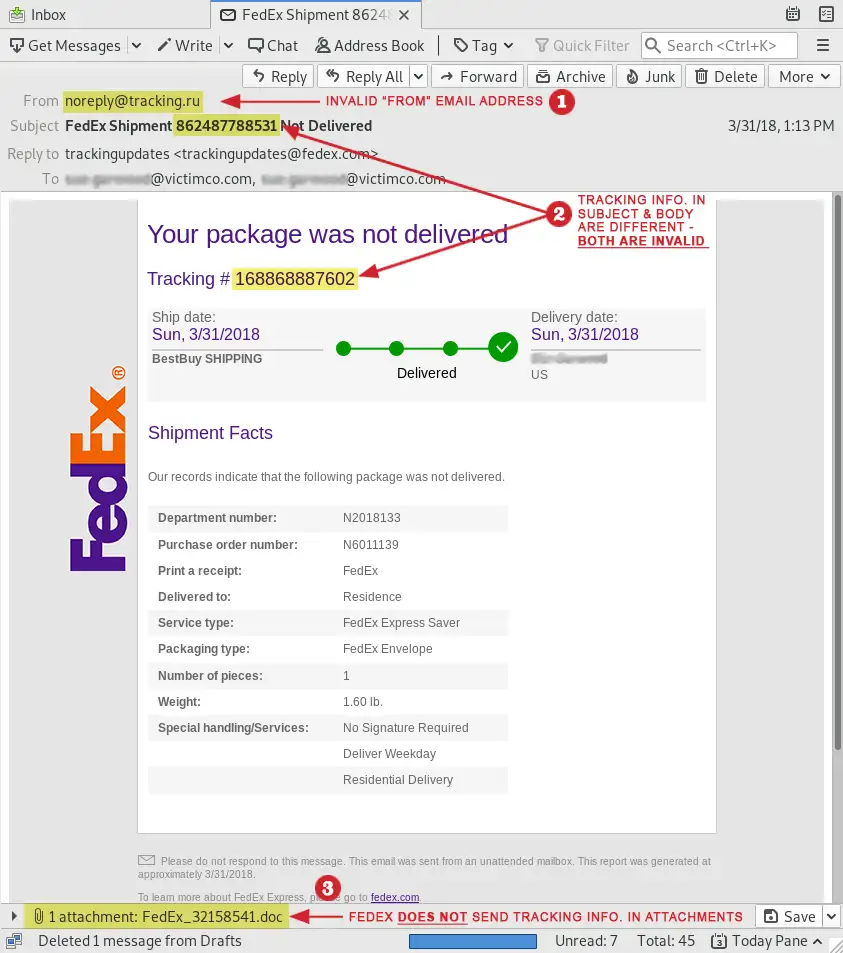
The image below is a spear phishing email identified and quarantined by Guardian Digital EnGarde Cloud Email Security. It closely mimics a legitimate FedEx shipment confirmation email. Can you spot the phish?
Some indications that this is a fraudulent email include the following:
- An invalid “From” email address
- Invalid tracking information, which differs in the subject and the body of the email
- A malicious attachment is located in the bottom left corner; FedEx does not send tracking information as an attachment.
Still have Questions?
What Is The Best Protection Against Phishing Attacks?
What Is The Best Protection Against Phishing Attacks?
There is more than one way to protect yourself from phishing attacks. You need to be aware of your users and have a security stack that checks all the points. This includes scanning links and attachments in real time, catching attempts to impersonate others, checking senders (yes, SPF and DMARC are still important), and keeping up with new threats as they appear.
How Can Businesses Improve Phishing Protection in 2025?
To prevent phishing attacks and scams in 2025, businesses need to combine training that you can do with tools that can change as threats do. Think about more than just surface screens. Think about finding malware, protecting against spoofing, and scanning that happens in real time. And your defenses need to stay just as smart as phishing techniques get smarter, especially since AI can now make fake websites and messages that look and feel real.
How Do Phishing Protection Tools Detect Malicious Emails?
Sender behavior, message structure, and embedded link or attachment content are just a few of the indications that advanced phishing protection technologies look for. Heuristic scanning, sandbox analysis, URL reputation checks, and artificial intelligence are some of the methods they utilize to identify dangers that are typically missed by standard filters.
These phishing protection tools work by analyzing multiple signals — not just content, but behavior, link structure, domain reputation, and spoofing indicators in real time.
What Should I Do If I Clicked on a Phishing Link?
Disconnect from the network, run a security scan, and alert your IT or security team immediately.
Final Thougths: Why Protection Against Phishing Attacks Takes More Than Awareness

Phishing attacks are so effective because they target the person, not the system. And while awareness is essential, protection against phishing attacks has to account for the moments when someone still clicks.
Some phishing attacks in your inbox will still get through. A convincing message, a fake login page, a well-timed request. That’s all it takes.
You need defenses built around the user. Real protection uses multiple controls working together. Not just one filter. Not just a warning banner. A strong email security platform can spot and block these threats as they happen. The good ones don’t wait for a signature update. They learn, adapt, and react in real time.
Prevention starts with seeing phishing attacks as a part of a system, not just a message. It is crucial to prioritize team email security training; strengthen your filters, and assume some attacks will get through.
“Engaging in email security best practices is important, but this alone will not prevent a successful phishing attack,” says Guardian Digital CEO Dave Wreski. “A fully integrated email security solution that delivers total end-to-end control is critical to safeguard business email accounts.”
The right system doesn’t just block spam. It catches the sophisticated threats. The quiet attacks. The zero-day lures. And it keeps evolving as the threats do.